MEC adoption parameters proposed for enterprise and CSP consideration

Praveen Gundkal of TechMahindra Ltd
Multi-access edge computing (MEC), formerly called mobile edge computing, is an ETSI-defined network architecture concept that enables cloud computing at the edge of a network. In layman’s terms it brings cloud advantages at the edge of the network or closure to customer services outside regular cloud deployments hereby reducing latency and bringing in efficiency.
The Edge of the network from the communication service provider (CSP) standpoint is within the Radio Access Network (RAN), says Praveen Gundkal of TechMahindra Ltd. This can be the LTE (4G) base station (eNodeB) site, small cells aggregation point or along the core network. Specifically, for 5G Standalone network a physical deployment of MEC can have single or multiple UPFs (User plane functions) configured to steer data traffic between MEC and Packet core data network e.g. MEC co located with UPF at a base station (gNodeB)
From an enterprise point of view, MEC physical deployment can be located at the multi-RAT cell aggregation site/s indoors within an enterprise (e.g. headquarters, large scale industry, hospital) or outdoor where there is a special coverage requirement. (e.g. football stadiums, arenas etc)
By doing so we are bringing cloud computing platform closer to where actually data is generated and processed. MEC will provide storage, processing, and analysing functions for data in a much faster way at the edge of the network. Applications which require real time feed, which need to process data and provide real time monitoring for enterprise to make decisions will be hosted in MEC. AI/ML/DL application processing will serve true value deployed at the edge of the network.
Four key MEC challenges (reference Gartner report) are:
- Data (Integration, Governance & Analytics)
- Diversity (Use cases, Topologies, Technologies & Standards)
- Protection (Security, Privacy & Compliance)
- Location (Scale, Environment, Remote Management & Autonomy)
With these challenges, how CSPs or enterprises can look at exploring MEC potential and determining a business model becomes crucial to achieve business value i.e. total cost of ownership, staff productivity, operational resilience, and improved user experience.
Figure 1 depicts MEC positioning for CSP and enterprise.
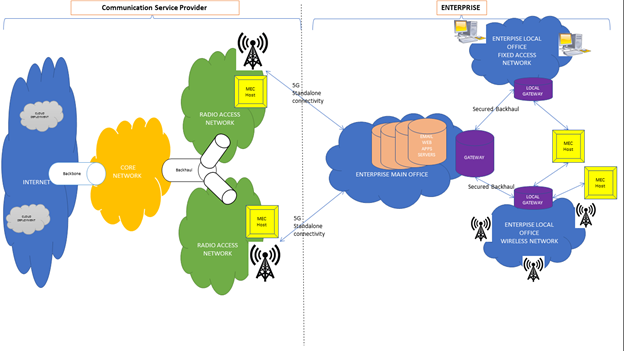
Below are 8 key parameters proposed for enterprise and CSP in conjunction for edge computing adoption, implementation and utilisation.
- Maturity
- CSP – Strategising and assessing current network maturity will be important e.g. how much is telco network cloud native? Is IT-BSS platform capable to support MEC application hosting aspects – provisioning, mediation & billing, support model, infra & tenant onboarding and assurance at radio network level. Assessment of Key technologies closely associated to create business and customer value – 5G, network slice, single OSS 5G inventory etc.
- Enterprise – Maturity assessment providing scores in terms of key enablers like NFV vs physical native applications, applications development, vendor flexibility for MEC integration & hosting, security and organisation compliance will help in MEC decision-making.
- NFV
- CSP – A variety of technologies are in use for different domains – Radio, Core, Transport, Packet core for data processing and communication network. How MEC can be used to bring uniformity, efficiency and scalability is to be investigated. Whether IT (BSS/OSS) and Network applications are virtualised? – 50%,75%, 100%. Is NFV environment in place for 5G Standalone launch and MEC hosting. Strategy and position on ORAN need to be considered in planning.
- Enterprise – Consideration of moving an NFV application from a Private On Prem, cloud or centralised Public cloud onto CSP MEC hosting, migrating application and customers from physical native applications from enterprise premises onto MEC into sizeable manner, a migration strategy with impact analysis needs to be devised.
- MANO (Management and Network Orchestration)
- Both for CSP and enterprise, MANO will be a challenge considering the variety and distribution of MEC cloud. As per ETSI, design of MEC cloud will need to divide distribution of control function partly centralised and partly in MEC. Robust set of APIs to be developed to interface and interact for management purposes.
- 5G
- CSP – Edge computing will enable 5G technologies for achieving performance KPIs. 3GPP 5G system specifications define the enablers for MEC. Options for hosting MEC depends on security, operational and use cases requirements. MEC colocation alongside UPF in RAN is to be worked out for traffic routing and policy control.
- Enterprise – Intelligent use of MEC based application and seamless use of 5G connectivity from CSP based on technical and business parameters like application functional and non-functional requirements, customer survey scores, real time solutions, scalability and overall cost will determine efficient technology usage.
- Data Model Enterprise/CSP
- CSP and enterprise will need to work on their data model where GDPR compliance and data privacy per location, region, country can be met using MEC hosting instead of a central cloud location.
- Use cases
- CSP – 5G slicing use cases with MEC for B2B segment. Data analysis and security for efficient utilisation of network resources.
- Enterprise – Idea is to build real time connect and provide seamless services to employees (internal) and customer (external). Use cases to consider will be Smart buildings/factories, Data Analysis real time using artificial intelligence (AI), video streaming, augment / virtual reality (AR/VR) conferencing.
- Mobility
- Both CSP and enterprise need to account for mobility of an Internet of Things (IoT) device. A UE like mobile phone or a device fitted in a vehicle, the challenge is meeting application requirement where location is variable but requiring real time analysis. Configuring MEC host within application usage radius and designing hosting accordingly is to be considered.
- Operational & Process impacts
- MEC will impact business process functions and overall operational model. Enterprise busines process function affected will be in service fulfilment and assurance areas. Key domain impacted will be Service domain relating to service quality management, service configuration management and problem management. CSPs’ IT Service Management e.g. Remedy or Service Now will need to cater for MEC specific out of the box solution per impacted process modules i.e. mainly Incident, Event, Change, Availability, Access, SLA, and Configuration management. Both CSP and enterprise will need to adopt Change Management framework for user adoption and training to ensure business change impact and user alignment is not at risk.
Conclusion
Enterprise is at the forefront to utilise MEC offerings from CSPs and this will enable several use cases to enhance CeX. However, the journey is long, stretched and challenging. The above parameters are aimed at providing a snapshot for 360-degree view considerations.
The author is Praveen Gundkal of TechMahindra Ltd.
About the author
The author is Praveen Gundkal of TechMahindra Ltd. He is a business consultant for Network Capabilities & Digital Transformation. He is currently working as service design architect enabling 5G capabilities for one of the leading UK CSPs. The reviewer is Dr. Anand Singh, CEO – ILINK Digital Advanced Communication Services.
Comment on this article below or via Twitter @IoTGN
